CHAPTER 2
Global Environmental Problems
1Altan DIZDAR1, 2Ertugrul DIZDAR2 & 3Cagan DIZDAR
1Civil Engineer Altan Dizdar, General Manager at ORKON INTERNATIONAL CO. altan.dizdar@orkon.info
2Agricultural Engineer Ertugrul Dizdar, Chairman of the Board at ORKON INTERNATIONAL CO. ertugrul.dizdar@orkon.info
3MSc.Civil Engineer Cagan Dizdar, Columbia University, New York USA, cagandizdar@gmail.com
Contents
- 2.Introduction
- 2.1. Climate Change
- 2.2. Water Resources Pollution/Depletion
- 2.2.1. Causes & Impacts of Water Resources Pollution/Depletion
- 2.2.2. Control of the Pollution of the Water
- 2.2.3. Reasons for the Droughts :
- 2.3. Loss of Biodiversity
- 2.3.1. Benefits of Biodiversity
- 2.3.2. Categories of Biodiversity
- 2.3.3. Convention on Biological Diversity
- 2.3.4. Causes & Impacts of Biodiversity
- 2.4. Land-Use Problems in Urbanisation, Agriculture & Forestry
Environmental problems, rather in relation to socio-economic issues, display a complex picture & can act on a global level. Global environmental problems endanger the sustainability of the environment without recognizing political boundaries; it is a threat to human beings, health, safety & productivity, survival of other species & food safety & water resources. Climate change, global warming, desertification, environmental degradation, destruction of the ozone layer, acid rains, air, water & soil pollution, depletion of natural resources, loss of biodiversity, destruction of the forests, sea & ocean pollution, acidification of the oceans, hazardous wastes, adverse conditions caused by the waste, the results generated by the erosion & unplanned urbanization problem are all among the global environmental problems. So, at an international level, attempts are taking place to solve these environmental problems altogether.
Environmental protection is heavily on the international agenda & these problems can only be solved by the efforts of the non-governmental organizations, public & private sectors, civil society, national efforts & international cooperation & also an important dimension of efforts to protect the environment is to increase public awareness & the participation of whole groups. The triggering nature of environmental problems requires coordination & synergy in the processes for solution efforts.
Figure 1. Global Environmental Problems

Initiatives to find solutions to environmental problems have gradually started to be on the agenda of the international community since the 1960s. The “1.5°C Global Warming” report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) states that, along with global warming, climate-based risks related to health, food safety, water desire, human safety and economic growth will increase. The main aim of environmental policies is to have social welfare to top possible level by keeping environmental quality at a certain level. Although environmental policies differ across countries, the main concept that stands out as a common goal is the “sustainable development”. While sustainable & economic and social developments are recorded, it is aimed to reduce the people’s affects on the environment by protecting the nature & supply a clean environment to future generations.
As a result of global environmental problems, Ozone Layer Depletion & Increased Ultraviolet Rays are detected where this ozone hole refers to the decrease in ozone volume in the stratosphere (ozone layer) in the spring since the late 1970s. Apart from this event in the stratosphere, ozone perforation is also observed in the troposphere in the spring.The main reason for ozone depletion is that atomic halogens destroy ozone molecules where the main source of these halogen atoms are artificial halocarbons (chlorofluorocarbons - CFC, freons & halons). After these compounds are released on the surface, they are transported to the stratosphere & the destruction mechanism begins & it has been observed that the ozone hole expands with increasing halocarbon emission. Because the ozone layer prevents the harmful ultraviolet rays that reach the world by filtering, the ozone hole has caused worldwide concern & the production of gases that damage ozone is prohibited by the Montreal Protocol. It is suspected that the ozone hole increases diseases such as skin cancer & cataracts, damaging plants & plankton. (Wikipedia)
The fact that environmental problems have a cross-border nature has made it necessary for international organizations such as the United Nations (UN), the European Union, the Organization for Economic Cooperation & Development (OECD), the European Security & Cooperation Organization (OSCE), World Meteorological Organization (WMO), NASA & other international bodies to work for the solution of these global environmental problems altogether.
Figure 2. Air Pollution, Dirt & Smoke on the City
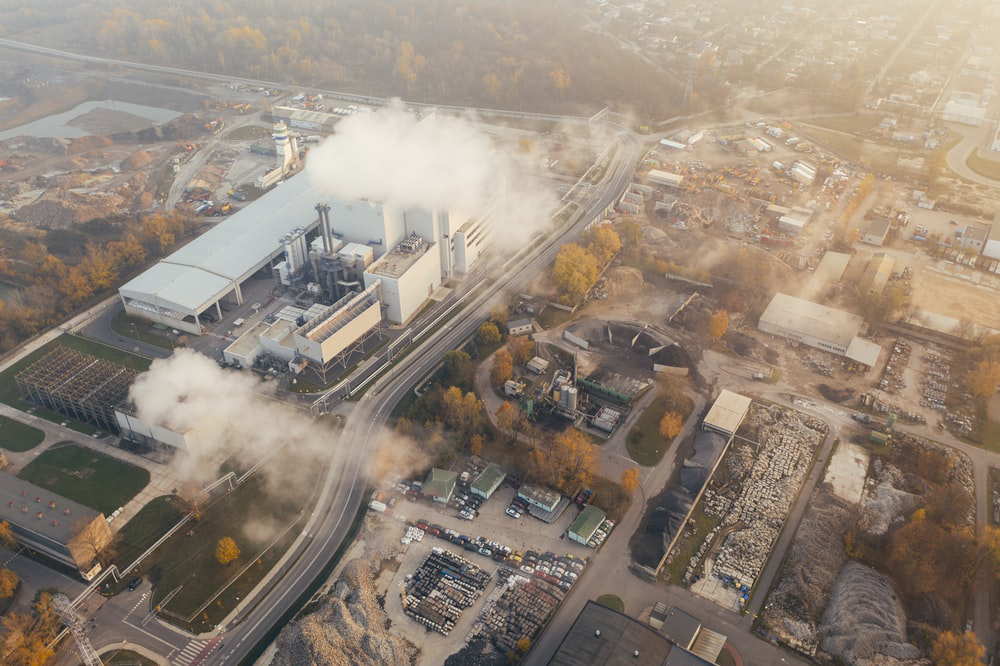

Source : https://unsplash.com/photos/uKvPDQop-JA
2.1. Climate Change
Climate change means when a change occurs in the world’s climate system & causes for new weathers. Changes in climate can occur over years because of various reasons but the most important reason happened because of the industrialization & climate has been mainly affected by the human beings’ activities & caused to global warming & climate change. (Wikipedia)
Since the mid-19th century, in addition to the natural variability in the climate, with the industrialization, a new period has begun & human activities also started to affect the climate. With the industrial revolution, the temperature increase that started to be seen on the earth & in the lower parts of the atmosphere (lower troposphere) due to the rapid increase in the accumulation of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere with various human activities such as deforestation, burning fossil fuels & industrial processes & with the urbanization & it is called “global warming”.
Human activities based on "incineration" such as energy production, heating, & transportation have accumulated the existence of CO2 & other "greenhouse gases" in the atmosphere, which has led to global warming by trapping the earth's heat.
The results of this fact are the rising of the level of the seas by the fusion of glaciers at poles & at high altitudes (some countries are flooded); Heavy droughts, floods, hurricanes take place as a result of immediate changes in temperature; the depletion of bacterial species, plant & animal. These results have started to show themselves.
Environmentalist groups state that these possible consequences can be as serious as the impact of a giant meteorite hitting the earth or a major nuclear war.
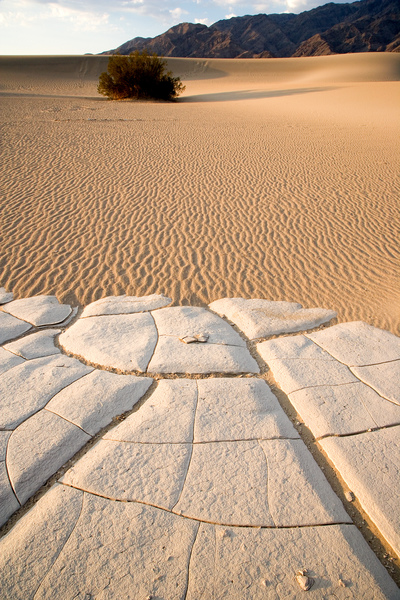
Figure 3: Desertification & Melting of Ices as a Result of Climate Change & Global Warming
 |
 |
|---|
Source : https://picspree.com/en/photos/cracked-and-rippled-desert-landscape-612521
Source : https://picspree.com/en/photos/ice-floes-in-the-arctic-ocean-603545
2.1.1. Causes & Impacts of Climate Change
As the causes of global environmental problems & climate change ; food scarcity, flooding, deadly heat, superstorms & widespread diseases are tried to be overcomed & precautions are taken for the problems brought by the modern life, such as transportation, land use, food & energy. report, the prominent findings as a summary were as follows: To analyse & state these problems, a Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C was prepared & published by the Intergovernmental Panel on climate Change & at this:
The 1.5°C limit, the warming of 1.5°C & above is especially important because it increases the risks associated with long-term & irreversible changes, such as the disappearance of some ecosystems with the examples below:
Figure 4. Hazards of Climate Change

2.1.2. Greenhouse Gases
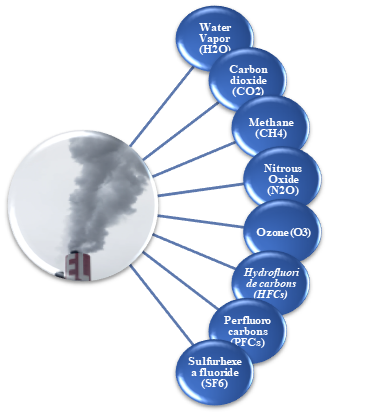
Various processes & substances can cause the Earth's average temperature to increase or decrease. The most important of these factors are the so-called greenhouse gases. It is known that the presence of these gases in the atmosphere causes the Earth to heat up about 32°C. If the Earth did not have an atmosphere, there would be no liquid water on its surface & the Earth would be an unfavorable planet. In this respect, it can be said that greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are beneficial. However, the increase in the amount of greenhouse gases can also cause climate changes & degradation of nature.
Water, which causes the greenhouse effect, is indispensable for living life on Earth. Ozone acts as a shield that prevents harmful rays from the sun, reaching to the earth. Other important greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide & methane. Retrospective studies show that in the last 250 years, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased by 36% & the amount of methane by 148%. It is thought that the main factor causing global warming is the increase in the amount of carbon dioxide & methane in the atmosphere.
Figure 5. Greenhouse Gases
Most of the increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is due to human activities. The use of fossil fuels in particular causes the release of large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. In addition, cement production is one of the important reasons of this increase. Two main methods that can be applied to prevent the increase in the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere as a result of human activities & to increase the effectiveness of biological processes using greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. For example, by increasing the number of plants using less fossil fuel or using carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, the increase in the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can be prevented.
2.1.2.1. How to Reduce Greenhouse Gases?
It is possible to reduce the Greenhouse Gas Emission Amounts by paying attention to the following items:

Technologies that provide energy saving in every field from industry to agriculture must be developed & the use of contribution to renewable energy sources such as solar (photovoltaic), geothermal, biomass & wind must be increased to overcome the climate change.
Figure 6. Windmills to replace fossil fuels; renewable energy sources like wind is one of the precautions needed to decelerate the climate change.
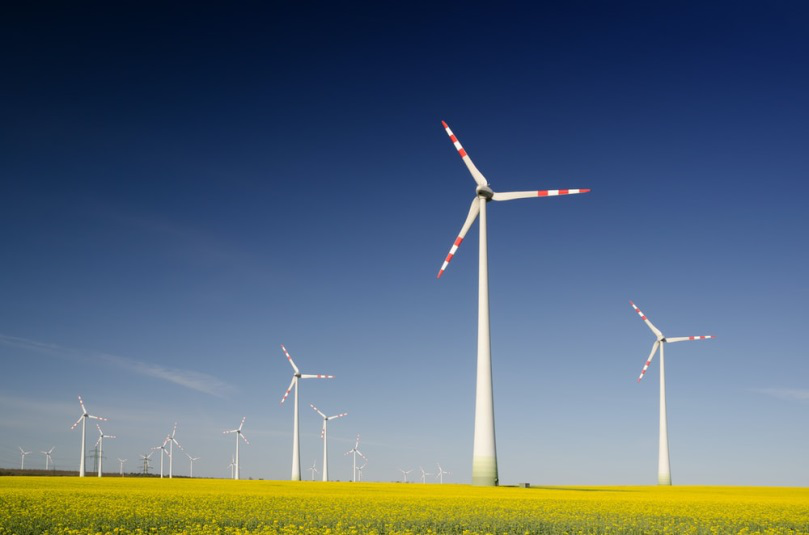

Source: https://unsplash.com/s/photos/windmill?ref=thestocks.im
2.1.3. Carbon Footprint
Each individual causes a different amount of carbon emission depending on where & how they live & each person’s carbon footprint is different than the other from the type of food they eat, to their mode of transportation & electricity consumption.
For example, the gas we burn while driving, the energy we use to heat the house & the production process of the foods we eat cause a certain amount of carbon dioxide emission.
Figure 7. Ecological Foot Print

Source : http://thestocks.im/
Figure 8. Causes of Carbon Footprint

2.1.3.1. How Can We Reduce Our Carbon Footprint?
We can reduce our carbon footprint by saving energy & changing some of our habits. For example, using public transportation such as buses or trains instead of driving will reduce the carbon emissions we cause. Using energy saving bulbs in our homes, strengthening the thermal insulation of our home, using renewable energy sources if possible is also effective in reducing the carbon footprint. Since cattle & poultry are also effective in greenhouse gas emissions, you can consume less red meat to reduce demand for these animals & thus production. In addition, trees absorb carbon dioxide & produce oxygen. For this reason, we can plant trees to pay our debt to the nature.
Organic or inorganic chemicals are the main causes of chemical pollution & the most common chemical pollutants are the compounds that are used in large areas & are permanent & do not vanish easily in nature. There are many chemicals that end our lives & harm our future generations without realizing what is in our lives. Insecticides used in agriculture are only a small part of these chemical poisons. In addition to these; materials used in dry cleaning activities, chlorinated solvents, oil refineries, coal plants, wrong construction, mining & transportation types are examples for these. Even the daily detergents we use in our home are chemical compounds that pollute the environment.
2.2. Water Resources Pollution/Depletion
Water exists in seas, oceans, rivers, lakes, aquifers & groundwater & water pollution is mainly caused by the activities of human beings such as urbanization, population growth & increased living standards & also influenced by changes in climate & natural conditions. Worldwide, human activities & natural forces are reducing available water resources rapidly. Now, at last, public's awareness of the need for better control & protection of water has increased & necessary precautions are tried to be taken by all countries. To overcome the pollution & depletion of water, authorities are increasingly evaluating the amount & quality of water & trying to coordinate the control & protection of the water resources.
Figure 9. Water Pollution
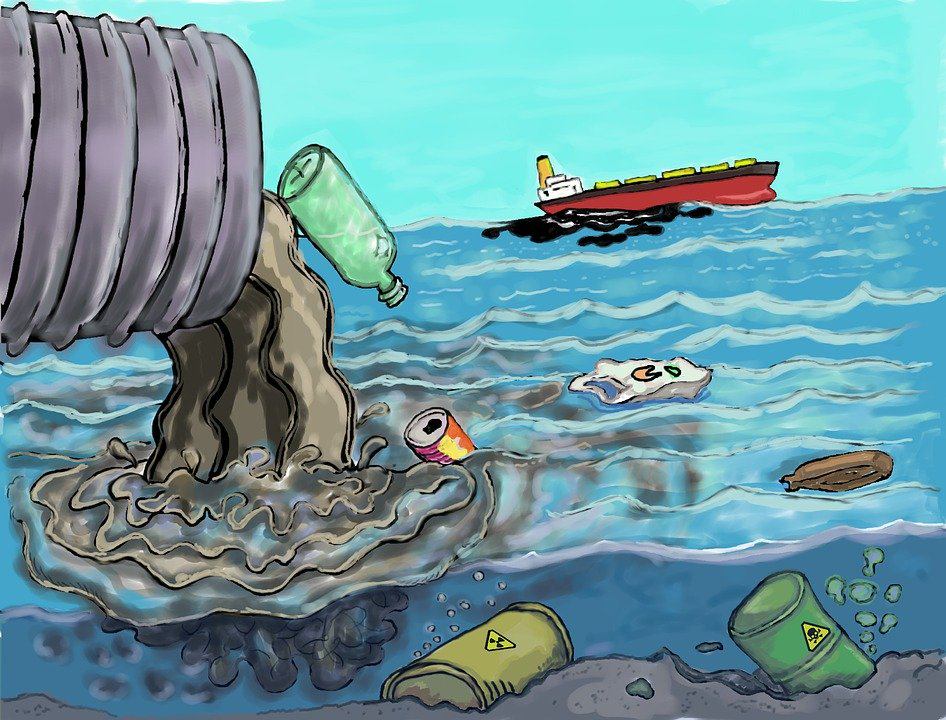

Source : https://pixabay.com/illustrations/pollution-trash-degradation-1603644/
For example,distribution of inadequately treated wastewater into natural water systems will lead to degradation of aquatic ecosystems. Also, this will lead to public health problems for the people & living things as this polluted river water may be used for drinking & irrigation. In the world, water pollution is the most important cause for the deaths & diseases around, e.g. due to water-borne diseases (Wikipedia).
Figure 10. Distortion of the environment will spread many diseases everywhere
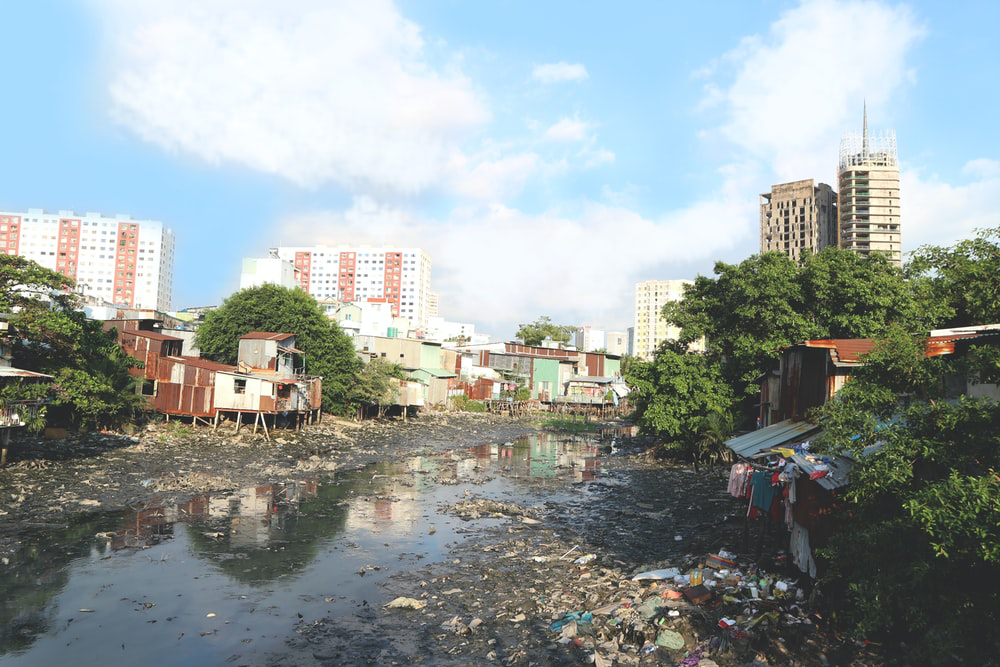

Source : https://unsplash.com/photos/Sj5vmEumehE
2.2.1. Causes & Impacts of Water Resources Pollution/Depletion
Environmental pollution can damage water resources & the water ecosystem. Rural changes such as environmental pollution, climate change, urban growth & deforestation have direct effects on ecosystems & on water resources. The main pollutants include, for example, organic substances in wastewater discharge & disease-causing organisms, fertilizers & pesticides from agricultural areas, acid rains from air pollution, heavy metals released as a result of mining & industrial activities & activities such as poorly managed farming, forest clearing, road construction & mining can result in large quantities of soil & poisoned particles remaining in the air & they finally merge in the rivers & water sources (sedimentation). This damages the water ecosystem, impairs water quality & prevents internal water transport.
Main consequences of water pollution is the disappearance of biodiversity & aquatic ecosystems where also due to deforestation, sediments & bacterias are appeared under the soil & therefore contaminate groundwater. Also, humans are harmed by the alteration in the food chain & get illnesses when drinking or using contaminated water. As water pollution has a great impact in the environment, we must ensure water availability, its sanitation & sustainable management.
The effects of drawing too much water from both surface water & groundwater are striking & it causes to water depletion. In the past decade, much more water has been drawn from underground springs & the benefits of using underground water are often short-lived, but their negative consequences - for example, low water levels & depleted resources - can continue for a long time. At the same time, climate change is also another reason for the water scarcity.
Figure 11. Main Factors Affecting the Water Pollution & Depletion

2.2.2. Control of the Pollution of the Water
In fact, the negative role of the industry on the environment is perhaps more than any other factor. Especially industrial enterprises cause liquid pollution & water pollution & indirectly due to water pollution, cause excessive pollution on soil & vegetation & cause rapid destruction of the environment.In addition, industrialization movements & migration to cities causes rapid & irregular urbanization cause to pollution & depletion.
In spraying of pesticides, water resources are contaminated with pesticides as a result of carrying airborne drug particles to the water by wind or discharging factory wastes that produce pesticides into water sources or rivers. On the other hand, the unconscious & excessive use of chemical fertilizers also make the soil barren over time & again creates negative effects with the natural cycle both with water pollution & other effects.
Storms, volcanoes & earthquakes also cause great changes in the water quality & to its ecology but these are not counted as pollution.
To control the pollution of water, it requires correct & appropriate management plans & infrastruture. Wastewater treatment plants belongs to the infrastructure system. Sewage & industrial wastewater treatment plants are usually established to protect water from untreated wastewater. Agricultural wastewater treatment for farms & erosion control at construction sites can also help to prevent water pollution. Nature based solutions are also another approach to prevent water pollution. (Wikipedia)
Figure 12. Pollution of the water
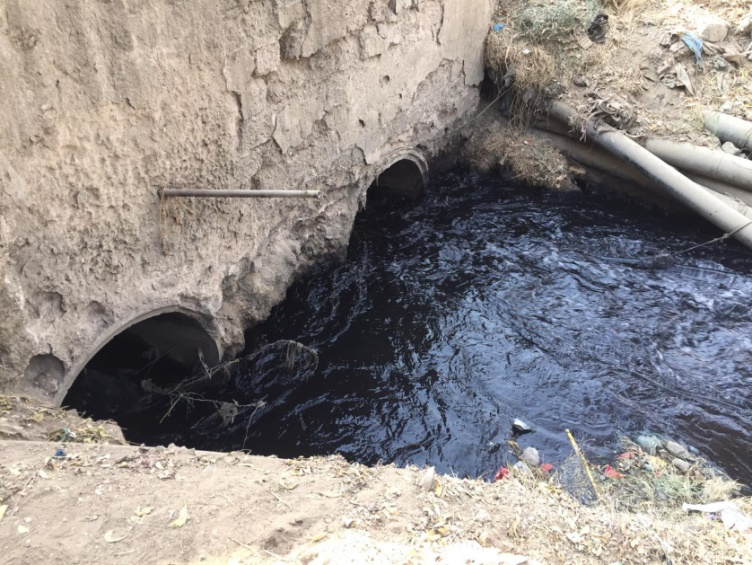

2.2.3. Reasons for the Droughts :
Drought is actually a normal & recurrent climate phenomenon that starts very slowly, develops for months or even years & affects very large areas & is different from other events. Occurs due to decreasing precipitation spread over one or more seasons. However, increasing temperatures & decreasing precipitation in many regions of the world as a result of global climate change increase the frequency & severity of drought events.
It causes serious economic, environmental & social impacts in very large regions & sometimes even in a whole country. Drought occurs in all climatic zones, but the vulnerability of the area to the drought & the degree of effects can vary greatly from one region to another. The causes of drought are easy to understand but their effects are difficult to predict!
The only reason for drought is not the climate change but the overuse, pollution of water resources, improperly planned water infrastructures & mismanagement are strongly influencial on this system & make the basins, countries & even economies even more fragile. It causes us to lose our all strength in front of such a drought & the consequences to be felt violently.
Drought, desertification & land degradation are important environmental tests of our age that may threaten the habitat & the most basic livelihood of the majority of the world's population & create a risk of food safety.
While the decrease in the amount of water is felt as an effect of drought, it also causes the failure to meet the increasing water demand or deterioration of the ecological systems. Besides their environmental effects, their economic effects can also be felt very heavily due to the severity of the drought. Sectors such as agriculture, energy, tourism & forestry are directly affected by drought. The cost of drought in Europe in 2003 was calculated as 11 billion Euros, in 2006, it was determined that the agricultural sector in Spain suffered more than 2 billion Euros due to drought.
In order for drought not to become a chronic problem, water resources should be managed well in both rainy & dry periods. Managing water resources at river basin scale is the first step to preserve the holistic structure of river ecosystems that are actually the source of water.
2.3. Loss of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the name given to ecological systems, species & gene diversity all over the world or in a certain habitat & the richness of plant & animal species & varieties in a region is called biological diversity & it provides the services necessary for the continuity of the economic & social life of human beings. Biodiversity is also important for ecosystem & nature provided services like flood protection, climate regulation, soil fertility, pollination & food, fuel, fiber & drug production.
Biodiversity loss is the depletion of animals & plants all around the world & also the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat whereas global depletion has so far been proven to be irreversible.
Figure 13. Prevention of Loss of Biodiversity is prerequisite for the survival of certain habitats.

Source: https://unsplash.com/photos/2xQcwGfGio8
Biodiversity is also the differentiation between land, marine & other aquatic ecosystems & living organisms from all sources, including ecological structures that are part of these ecosystems. Biological wealth or biological diversity refers to the diversity & variability of living things, their interactions with the complex ecological structures they live in, with each other & with their environment.
2.3.1. Benefits of Biodiversity
People have reached today's level in agriculture & technology as a result of biodiversity & wealth. The benefits of biodiversity & ecosystems are essential for the continuation of today’s high standard human life. The plant & animal species that make up the biodiversity are used in agriculture, pharmacy, medicine, animal husbandry, forestry, fishery & industrial areas, also in providing clean water & air. The high number & diversity of plant & animal species that make up biodiversity also provide economic gain to the country. Biodiversity balances ecosystems, makes the planet habitable, supports people's health, the environment & ecosystems.
Figure 14. Classification of Benefits of Biodiversity

Benefits of Plant Diversity: Plants clean the air, prevent erosion, add organic matter to the soil, & relieve soil fatigue. They provide shelter & nutrition to other living things & provide continuity to the ecosystem.
Benefits of Animal Diversity: Humans have used animals for guinea pigs, as a source of food by hunting & domesticated animals from ancient times until today. Some insects provide pollination of plants, ensuring the continuity of plant life & diversity, & thus the continuity of the ecosystem. A significant part of the insects ensures that the organic matter is decomposed & brought back to soil. Some insect species are also the food source of animals such as birds, fish, reptiles.
Benefits of Ecosystem Diversity: Nature based tourism is called eco tourism. Eco tourism has an increasing importance in recent years. Depending on the technological advances & lifestyle, people under stress rest themselves in nature. Stress is relieved by going to national parks & nature.
2.3.2. Categories of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is considered in 3 hierarchical categories according to
Figure 15. Categories of Biodiversity:

Biological diversity is the basis of living resources, which have an indispensable place in meeting the basic needs of people, especially food. The basis of all cultivated cultivars, that is, cultivated plant & animal species, is based on their wild relatives in nature. Today, wild species are used to obtain new types of agriculture or to improve the existing ones according to the needs of people. Ecosystems have also acquired complex & different structures & functions depending on environmental conditions as a result of the interaction of living & inanimate beings with each other & within themselves in order for wild species to survive, evolve, diversify & acquire new genetic features. It performs important functions in the continuation of natural balances such as integrity & diversity of ecosystems, climate, precipitation regime & species sociology.
Living resources, which are important for food & agriculture & are decreasing gradually, are among the important advantages that a country can have today. The areas of the world that can be cultivated & the water resources are rapidly polluting & disappearing. Scientists are of the opinion that in the near future, people will face a serious food problem. Developed countries are investing heavily in the development of new high-yield seed & breeding varieties & making efforts to retain food trade. In the light of these developments, the biological diversity of the countries becomes a great power, especially in terms of genetic resources. Because wild cultivars are used to develop varieties that are resistant to environmental pressures & have high production potential.
2.3.3. Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity is international legally-binding treaty, signed by the countries & aimed to promote sustainable development.The idea was more than protecting the animals, plants, micro organisms & their ecosystems but also to think about the people & their need for food security, medicines, fresh air & water, shelter & a clean & healthy environment to live in.
The three main objectives of the Biodiversity Convention (CBD) are:
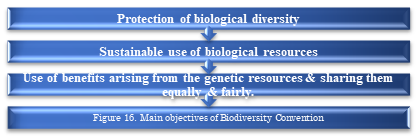
The Convention specifies that each country needs biological resources that need special protection measures & biological resources that have greater potential for sustainable use; It requires identifying & monitoring the categories & processes of actions that may have a negative impact on conservation & sustainable use.
2.3.4. Causes & Impacts of Biodiversity
We are now witnessing a continuous loss of biological diversity that affects natural life & human well-being. The main causes of this loss are changes in natural habitats due to intensive agricultural production systems; build; quarry activities; excessive use of forests, oceans, rivers, lakes & soil; pollution & increasing global climate change. The great role played by biodiversity in the sustainability of our world & lives makes its ongoing loss more & more unsettling.
In Europe, with the spread of agriculture & animal husbandry for 5000 years, human activities have shaped biodiversity. However, the agricultural & industrial revolutions over the last 150 years have led to sudden & increasing changes in land use, intensification of agriculture, urbanization & land evacuation. This has led to the loss of many experiences (eg traditional farming methods) that support the conservation of landscapes rich in biodiversity.
Europe's high per capita consumption & waste production mean that our impact on ecosystems extends beyond our continent. The European way of life is based on the intensive import of resources & goods from all over the world, which often causes unsustainable use of natural resources outside Europe.
Global & European Union 2020 targets aiming to stop & increase the loss of biological diversity are quite ambitious. Achieving these goals requires implementing effective policies, cross-sectoral coordination, ecosystem management approaches & a better understanding of the value of biodiversity.
EU policies on the subjectAlthough the goal of stopping the loss of biodiversity is accepted at various levels where the goal has not yet been met, even setting such a target has certainly raised social awareness. Since 2001, policies addressing biodiversity loss & indicators evaluating development have improved significantly.
The EU's 2020 Biodiversity Strategy will enable further integration of the work required to protect biodiversity into the development & implementation of sectoral policies. With its six objectives, this Strategy includes nature (target 1), ecosystems & restorations (target 2), sustainable use of the nature of Europe, land & marine resources through agriculture, forestry & fisheries (targets 3 & 4), alien species (target 5) & It addresses the global effects of the EU (target 6). The Biodiversity Strategy helps to meet the natural capital targets of the 2020 7th Environment Action Program. The main slogan of the Seventh Environment Action Program (7th EAP), which came into force in January 2014 & will guide Europe's environmental policy by 2020, is "Living well within the boundaries of our planet". Both strategies & programs have a long-term vision that will last until 2050.
Vision of the Biodiversity StrategyUntil 2050, the European Union biodiversity & the ecosystem services it provides - its natural capital - are preserved, valued & properly restored due to the essential value of biodiversity & their significant contribution to human well-being & economic well-being, thereby avoiding destructive changes caused by loss of biodiversity.
The main goal of the Biodiversity StrategyOn the one hand, to prevent global biodiversity loss & ecosystem degradation by 2020, & to repair as much as possible, on the other hand, to increase the EU's support to stop the loss of biodiversity.
The 2020 Biodiversity Strategy has further increased expectations in the light of the lessons learned from the implementation of the 2006 EU Biodiversity Action Plan. In addition, it has been implemented in full compliance with the UN Convention on Biological Diversity, which is the most important global biodiversity policy aimed at stopping biodiversity loss & thus ecosystem services loss until 2020.
Figure 17. Protection of sea & fishes with the plants

Source : https://unsplash.com/photos/jPFqcpfn_Fw
Natural parks, natural habitats should be created, organic farming should be preferred & people should be educated on these issues in order to include the generations of these creatures, whether they are plants or animals.
Farmers should be made aware of the negative effects of overgrazing, over-harvesting of plants & destruction of forests to gain land in terms of biodiversity. Destruction of coastal habitats & excessive & uncontrolled fishing must be prevented.
In addition, mechanisms for the protection & control of these species should be developed.
Biodiversity is the common wealth of the whole world. Biodiversity needs to be preserved in order to be able to transfer this diversity to future generations by meeting today's needs.
2.4. Land-Use Problems in Urbanisation, Agriculture & Forestry
In Land-Use, most problems arise from Urbanisation, Agriculture & Forestry & these problems must be solved by taking careful precautions. Rapid population growth in the world increases the pressures on the natural environment. With the speeding of urbanization & industrialization process, the natural environment is significantly polluted & consumed. Cycles in the natural environment are severely interrupted, deteriorated & causing problems that are difficult to solve day by day due to wrong land use. Unenvironmentally & unsustainable planning & the projects produced accordingly make the world more risky & uninhabitable for all living things. Especially the opening of areas that are risky in terms of natural disasters & which are not suitable for settlement cause an increase in life losses & material damages caused by natural disasters.
Due to global climate change, urbanization & wrong land use, damage caused by floods, erosion, droughts increases day by day. Thus, disasters, which are mostly caused by natural processes, turn into disasters of human origin due to human activities.
Agriculture is also heavily effected especially by the lack of infrastructure & misuse & faces the threat of land’s desertification & erosion. Forests must be protected & they mustn’t be opened to residentials & at most attention must be given to prevent the forest fires.
2.4.1. Types of Lands & Their Usage
Types of Land-Use & Types of Lands are defined in Figure 18. Types of Usage of Lands & Types of Lands, Correct Land-use must be chosen from the Correct Land Type:
 |
 |
|---|
Soil, which is one of the most important elements of the ecosystem, is very important in terms of its non-renewability & indispensable place of human & living life, as well as ensuring the continuation of the primary chain of vegetative production, the food chain that expresses the survival of herbivorous & carnivorous life. Soil, among other natural environment elements, faces more serious problems in terms of purchasing, selling & renting.
Incorrect land use means that lands are not used according to their ability capabilities. In other words, it is the use of lands without taking into account the geological, geomorphological (slope, topography, aspect etc.), vegetation, hydrological & soil properties. In addition to the pressure of the population, the decisions taken by the political authority have been effective in the “wrong land use”, which expresses the unconscious & overvaluation of the potential of the natural environment.
The land, which has many ecological, economic & social functions in the realization of sustainable development, is a limited resource & its use is limited by the climate, soil, geological & geomorphological structure of its location. It is sensitive to natural events & human activities, it is easily disrupted & loses many functions when used without care.
Land use & benefiting from the land means, firstly usage of the land for agriculture & forestry, then all kinds of land use, including making residential areas, utilizing for transportation, making trade, art, industry, commercial activities & holiday places.
Natural resources are left to the next generations by being further developed without consuming. Where agriculture will be made; where will the animal be grazed, where will be forested, where will litter be poured? When these questions are solved, renewable resources are not damaged. A new city is not established on agricultural land; a mountain skirt that needs to be afforested does not open to settlement. Land use plans are of great importance & are strictly implemented. Therefore, other than natural disasters, anthropogenic disasters will not be observed in the modern world.
Figure 19. Proper Urbanisation & Increase of Population is important in Land-use

Source :https://unsplash.com/photos/3ttFTqPQs5A
Land capability classification for basic soil studies & planning based on climate conditions must be done by combining usage & conservation data to determine the most suitable use of the land without causing soil degradation.
To take a decision on a land-use, the past & present applications of land use in a field must be determined & analyses must be done on how it should be in the future according to its current potential. Paralel with the natural & human resource determination made in the areas to be used in land use planning, it is defined as “land use decision development” to provide concrete suggestions on how the existing land use will be in the most appropriate form depending on the analyzes done (SWOT analysis).
Figure 20. Agriculture is prerequisite for food scarcity & Forests are necessary for a clean environment.
 |
 |
|---|
Source : https://unsplash.com/photos/2UqMez6xpQ0 ; https://unsplash.com/photos/F_hft1Wiyj8
2.4.2. Causes & Impacts of Land-Use Problems
General Causes of Improper Land Use can be summarized as follows:

The opening of agricultural areas to settlements & industrial facilities & the misuse of agricultural lands is a basic problem for land degradation. Because of the rapid urbanization which have started to be seen with the rapid population growth in the world, have become a threat to the world life & non-suitable settlements are started to be opened on productive lands, destroying the nature & the environment. Construction of airports in alluvial lands, construction of dams, roads, factories, tunnels, channels, etc. to first class agricultural lands & the misuse of productive agricultural areas is the main causes of land degradation.
The filling of the coastline & the area behind it with secondary residences & tourism facilities causes degradation of the lands & loss of area against the use of agriculture, grazing & forestry purposes.
Opening areas not suitable for agriculture & settlement to agriculture & settlement & opening sloping areas that are not suitable for agriculture to agriculture, grazing accelerates erosion, so the soil-plant-water balance turns upside down. In such areas, erosion reduces the yield value. This situation will not work in terms of agriculture, forestry & stockbreeding.
Acid rains from fossil fuels, industrial, mineral, domestic & nuclear waste, etc. causes the land to be degraded chemically & biologically. Pollutants that reach the soil from various sources (industrial & domestic wastes, pesticides & fertilizers, tanks & pipelines where oil products are stored, leaks from machinery & vehicles, etc.) cause various environmental problems & make the surface, ground & groundwater unusable for agricultural purposes, leads to product loss, shrinkage of the product pattern, degrading the quality of the soil & decreasing the yield value of the land.
Overgrazing that is animals eating the grass until the soil level & early grazing that is opening grassland before full growth to grazing & weakening of grass cover; directly leads to a decrease in the yield value of the land. As a result of overgrazing in the world especially in semi-arid regions, both the yield power of the grasslands decreased & the erosion events gradually increased. Also grazing in forest areas will lead to destruction of the forests & will cause to fires.

Source : https://unsplash.com/photos/7Je8Q8f-rmE
Excavations for mining purposes from the areas on land, especially forest, grassland & agricultural lands are among the reasons for wrong land use. Wells, galleries etc. opened after mining excavations & failure to cover up, exposure of soil losing natural vegetation against water & wind erosion may cause negative consequences. The effect of land degradation caused by mining is enormous & leads to irreversible consequences.
Figure 22. Distortion of the soil, as a result of Mining activity, the soil becomes bare & useless and hills are formed because of excavations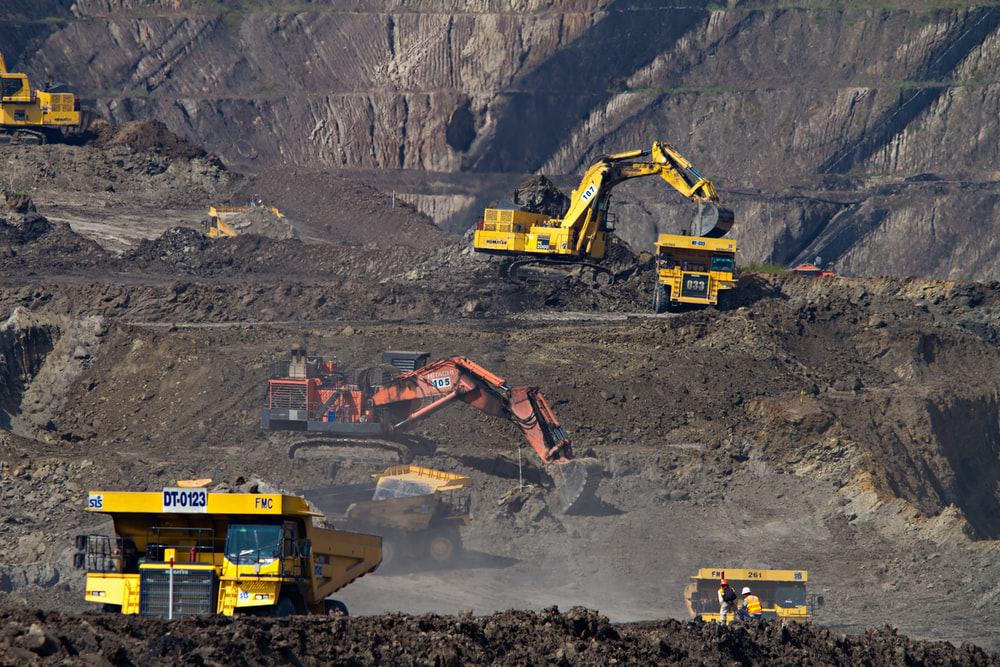
Source : https://unsplash.com/photos/Mk2ls9UBO2E
Over-unconscious application of agricultural spraying-fertilization, over-unconscious irrigation, use of wrong equipment, stubble burning, etc. pollutes the lands & turns lands open to erosion.
Passing roads through productive agricultural areas/forests & passing highways through flat plains & valley floors is among the reasons for wrong land use. According to the ideal land use planning, roads should be located at the intersection of flat areas & mountainous areas (settlements, landslides, slopes without earthquake risk) along with settlements.
The only reason for the destruction damage that occurs in the upper parts of the streams & the resulting loss of life is the housing inside the stream beds therefore in the design of the settlements, this condition is very important & must be respected.
Dropping solid & liquid garbage to random lands (wild storage) is among the reasons for wrong land use & is effective in losing the land's yield value. The main physical processes of wrong land use occur due to water & wind erosion, losses & other adverse changes in the soil occurs.
Erosions are very important; if no precautions are taken, serious problems can arise. Water erosion is the most effective & widespread type of erosion that causes land degradation among other types of erosion (wind erosion, glacier & wave erosion, avalanche & mass movements, etc.). The excessive cutting of forests for commercial purposes causes the effect of water erosion to worsen ; it is also common for forests to be burned down for reasons such as opening fields for obtaining settlements, tourism construction, etc.
Another wrong way of land use that leads to the decrease of the yield value of the soil or the land & the deterioration of its quality is soil contamination. Soil pollution is generally caused by air, water pollutants & agricultural activities. Soil pollution, one of the environmental problems, is also considered as a type of land degradation, as it reduces the yield value of the soil. Factors causing soil pollution; unconscious & extreme in agricultural fields. The use of pesticides, artificial fertilizers, industrial wastes & toxic substances released from various applications, wastes of mineral processing plants, sewage waters, wastes of industrial facilities, exhaust gases, pesticides used to combat fertilizers & harmful organisms.
Figure 23. As a result of improper land use, the land loses its yield value by passing through certain stages & transformed into useless areas in terms of agriculture, forestry & animal husbandry.

If these rules are not respected, wrong land-use will lead to erosion, flood, landslide, desertification & land degradation & afterwards a complete ruin of the environment will occur which will not be irrevertable.